(a) Macroscopic features
(b) Microscopic features
Figure 1 Characteristics of fractures of plastic fractures
Failures caused by brittle fractures refer to the failure of valve parts that suddenly fracture without obvious plastic deformation at the fractured part. Wenxiang Xu observed the macroscopic characteristics of the brittle fracture of the valve stem of the high-pressure main steam valve stem, and found that the fracture surface was smooth without fatigue sources; the entire fracture surface is rough, and the crack propagated along the thinnest position, as shown in Figure 2(a). Liqin Zhou and others observed the microscopic characteristics of the brittle fracture of the valve stem of the electric gate valve, and found that the fracture surface was lamellar with a river pattern, as shown in Figure 2(b). The valve parts will fail due to stress corrosion cracking especially when the environmental medium is a corrosive. Fractures caused by stress corrosion cracking refers to the breaking of valve components under the combined action of tensile stress and corrosive media.
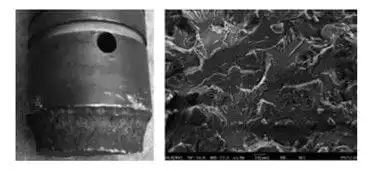
(a) Macroscopic features
(b) Microscopic features
Figure 2 Characteristics of brittle fractures
Failure caused by fatigue fracture refers to the fracture of valve components after a period of cycles under the action of alternating stress. Shaoxin Zhou and others analyzed the macroscopic characteristics of the fatigue fracture of the distribution valve spring, and found that the angle between the fracture surface and the longitudinal direction is 45°; the fracture surface can be divided into the crack source area, the crack propagation area and the transient break area. Among them, the surface of the crack propagation area and crack source area is smooth, while that of the transient area is rough, as shown in Figure 3. Jinhong Xie analyzed the microscopic morphology of the butterfly valve disc with fatigue fracture, and found that there were steps in the crack source area and fatigue striations in the crack propagation area, as shown in Figure 4.
Many parts break and fail in the valve. Among them, the valve stem has the highest frequency of fracture, and the necessary monitoring of the deformation of the valve stem should be carried out. In addition, from the above studies, it can be found that the fracture surface's characteristics are important clues to distinguishing different failures of valves.
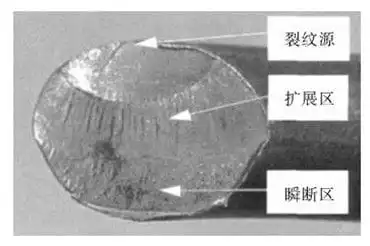
Figure 3 Macroscopic characteristics of fractures of fatigue fractures
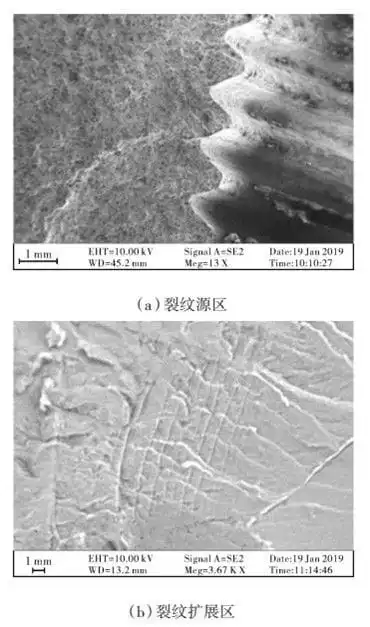
Figure 4 Microscopic characteristics of fractures of fatigue fractures
Reasons for failures caused by fractures of valves
Table 2 summarizes the research on the causes of fractures by domestic and foreign scholars. It can be seen from Table 2 that the factors affecting plastic fracture include structure and loads. The factors affecting brittle fractures include materials, structure, processes and loads. The factors affecting fatigue fractures include materials, structure, processes and loads. The factors that affect the failure of stress corrosion cracking include environmental factors, materials, structure and processes.
Table 2 Analyses of cases of failures caused by fractures
| Researchers | Fractures | Failure parts | Reason for failures |
| Linghui Deng | Failures caused by plastic fractures | Check valve discs | Stress concentration happens on the edges and exceeds allowable yield strength. |
| Pei Gao | Failures caused by brittle fractures | Spill valve flanges | Materials contain high carbide and make the material brittle. |
| Xuexing Zhang | Failures caused by brittle fractures | Electric valve stems | Improper quenching and tempering reduce the performance of the valve stem. |
| Chunrong Tang | Failures caused by fatigue fractures | Snifter valve seats | Spheroidizing annealing makes the material’s tensile strength lower. |
| JALALI | Failures caused by fatigue fractures | Globe valve bodies | Stress concentration |
| GAN | Failures caused by fatigue fractures | Brass valve bodies | Residual stress from brazing promotes microcracks. |
| Jun Zhang | Failures caused by fatigue fractures | Check valve bodies | Excessive temperatures for heat treatment reduce the impact toughness of the material. |
| EJAZ | Failures caused by fatigue fracture | Throttle valve stems | Great partial stress causes stress concentration. |
Among the environmental factors, the corrosive medium will damage the surface of the parts, and easily produce initial micro-cracks. At the same time, the mechanical properties of the material will be reduced. The corrosion effect should be taken into account in the design. Among the structural factors, stress concentration is the common cause of all failures caused by fractures. The initial micro-cracks caused by stress concentration are most commonly seen, and will still occur repeatedly after the replacement of parts. The improper operation of the process reduces the mechanical properties of the material and eventually leads to fractures and failures. Materials often act with processes or the environment, there are fewer failures caused by defects of the material itself. Among the loads, the load that the valve is subjected to under abnormal working conditions often exceeds the allowable stress of the material.
Next: Failures Caused by Wear of the Valve
Previous: The Selection of Chemical Valves
